| [1]Cilento BG, Freeman MR, Schneck FX,et al. Phenotypic and cytogenetic characterization of human bladder urothelia expanded in vitro. J Urol. 1994;152(2 Pt 2):665-670.[2]Lai JY, Yoon CY, Yoo JJ,et al. Phenotypic and functional characterization of in vivo tissue engineered smooth muscle from normal and pathological bladders. J Urol. 2002;168(4 Pt 2):1853-1857.[3]Liu JY, Peng HF, Gopinath S,et al. Derivation of functional smooth muscle cells from multipotent human hair follicle mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16(8): 2553-2564.[4]Drewa T. Using hair-follicle stem cells for urinary bladder-wall regeneration. Regen Med. 2008;3(6):939-944.[5]Atala A. Bladder regeneration by tissue engineering. BJU Int. 2001;88(7):765-770.[6]王涌泉,甘秀国,安瑞华,等.膀胱无细胞基质移植物重建同种异体兔膀胱的研究[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(18):1219-1222.[7]Fu Q, Deng CL, Liu W,et al. Urethral replacement using epidermal cell-seeded tubular acellular bladder collagen matrix. BJU Int. 2007;99(5):1162-1165.[8]Wallis MC, Yeger H, Cartwright L,et al. Feasibility study of a novel urinary bladder bioreactor. Tissue Eng Part A. 2008; 14(3):339-348.[9]Atala A, Bauer SB, Soker S,et al. Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet. 2006;367(9518):1241-1246.[10]Yang B, Zhang Y, Zhou L,et al. Development of a porcine bladder acellular matrix with well-preserved extracellular bioactive factors for tissue engineering.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(5):1201-1211.[11]任鹏程,张旭东,吕海港,等.脱细胞膀胱黏膜下层支架材料的生物学评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(8): 1365-1368.[12]王祝迁,木拉提•热夏提,李佳,等.大鼠触须毛囊干细胞的分离培养和鉴定[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(27): 5031- 5034.[13]Drewa T, Joachimiak R, Kaznica A,et al. Hair stem cells for bladder regeneration in rats: preliminary results.Transplant Proc. 2009;41(10):4345-4351.[14]Piechota HJ, Gleason CA, Dahms SE,et al. Bladder acellular matrix graft: in vivo functional properties of the regenerated rat bladder. Urol Res. 1999;27(3):206-213.[15]张丽萍,杨嗣星,王玲珑.膀胱细胞外基质的研制[J].武汉大学学报:医学版,2004,25(3):339-341.[16]Kim BS, Putnam AJ, Kulik TJ,et al. Optimizing seeding and culture methods to engineer smooth muscle tissue on biodegradable polymer matrices. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1998; 57(1):46-54.[17]Sypniewski D, Machnik G, Mazurek U,et al. Distribution of porcine endogenous retroviruses (PERVs) DNA in organs of a domestic pig. Ann Transplant. 2005;10(2):46-51.[18]Martin Y, Vermette P. Bioreactors for tissue mass culture: design, characterization, and recent advances. Biomaterials. 2005;26(35):7481-7503.[19]徐明曦,周哲,张明,等.人脂肪来源干细胞与胶原支架共培养的实验研究[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2012,8(4):189-194. |

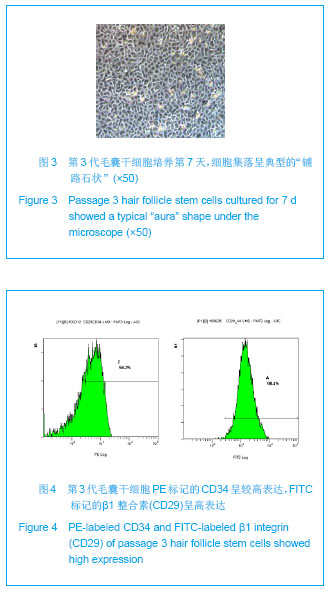

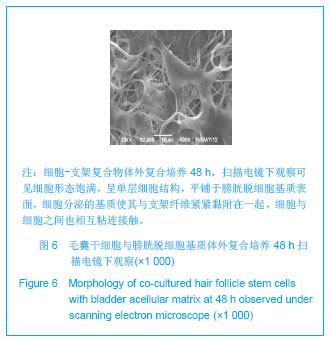
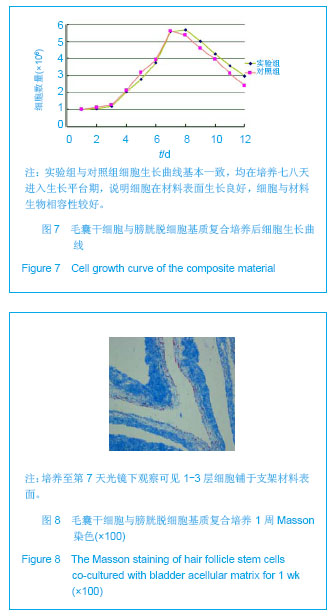
.jpg)